"Seru Seisan, also called “beyond lean” in many Japanese manufacturing industries, is an innovation of the production management mode in Japan. Although an increasing number of manufacturing enterprises in Japan have been adopting this strategy with great success, it is not popular among manufacturing enterprises and researchers out of Japan.Trechos retirados de "Seru Seisan- An Innovation of the Production Management Mode in Japan" publicado por Asian Journal of Technology Innovation 18, 2 (2010)
...
Mass production, symbolized by the conveyor line, is a kind of universal production management mode that has been widely adopted by numerous manufacturing enterprises all over the world. The long history and popularity of the conveyor line influenced peoples’ minds. Implementing the conveyor line in manufacturing industries, especially in final assembly processes, became a constant thinking pattern. Hence, people could not imagine that a high performance production management mode was rising in Japan and gradually taking the place of the conveyor line in some manufacturing fields.
.
Over the past decade, several Japanese manufacturing enterprises have dismantled their conveyor lines and adopted Seru Seisan.
...
Seru Seisan is an innovation of the production management mode in Japan. It emerged from a very complicated environment of mixed factors both in and out of Japan. The main factors are as follows.
.
Change of demand to high variety and low volume [Moi ici: Aquilo que caracteriza Mongo]
.
Demand changes are embodied in two main aspects: product variety and product volume. From the standpoint of product variety, the diversified and personalized demand leads to high product variety. The shortened product life cycle also results in diversified products. Moreover, fluctuations in customer demand have negative effects on product volume.
.
The efficiency of the conveyor line will dramatically decrease when confronted with variable and fluctuating demands. Therefore, highly efficient but less flexible conveyor lines should be urgently replaced by manufacturing organizations pursuing high flexibility. In Japan, Seru Seisan is currently regarded as the most powerful approach in some manufacturing industries to deal with the dynamic environment with high product variety and low product volume.
.
Low flexibility of the conveyor line.
The conveyor line is popular in the final assembly processes of mass production systems due to its high efficiency. Its other advantages include high productivity, superior product quality, low product cost owing to economy of scale, and low labor cost by low-skilled workers. ... The major demerit of the conveyor line centers on its lack of flexibility. Almost every conveyor line is designed for one or several specific product types. Therefore, measures should be taken to reconstruct the line when the product type changes. Meanwhile, it is essential to adjust the line in order to obtain high performance against the fluctuating demand volume.
...
Long period of economic stagnation in Japan after 1991.
The expansion of automation was curbed in the 1990s because manufacturing enterprises could not afford the additional enormous amount of capital investment required for automation during the economic recession. Moreover, managers gradually realized that high-cost automation could not always bring the sound effect as expected because of unstable customer demand. Therefore, the requirement for low-cost but highly efficient systems arose reasonably under the influence of an external economic factor and an internal performance factor.
.
The economic stagnation of the 1990s prompted Japanese manufacturing enterprises to dismantle their highly efficient conveyor lines and begin to innovate on their production management mode."
sexta-feira, setembro 01, 2017
Seru (parte V)
Parte I, parte II, parte III e parte IV
Prisioneiros do século XX
"Os custos unitários de trabalho são um factor crítico para a nossa competitividade e não podem ser dissociados da produtividade, intimamente ligada a qualificação profissional e às leis laborais, áreas onde tem de haver um esforço continuado de adaptação às necessidades das empresas."Quando escrevo sobre as mentalidades atoladas no século XX, prisioneiras de um passado que formatou mentalidades quando se tinha 20 anos, é disto que escrevo.
A promoção da concorrência imperfeita e dos monopólios informais é a descoberta, e a busca das condições, em que uma empresa consegue fugir desta armadilha mental de que tudo se resume ao custo.
De um lado: não podemos ser competitivos com estes custos!
Do outro lado: como podemos ser competitivos apesar destes custos!
Trecho retirado de "Os recursos humanos e a competitividade"
BTW:
- o recente "The Myth of the Skills Gap"; e
- o clássico deste blogue, "Ainda acerca da formação profissional"
O contexto tem muita força (parte IX)
Parte I, parte II, parte III, parte IV, parte V, parte VI, parte VII e parte VIII.
Imagem e trechos retirados de "Contrasting Perspectives of Strategy Making: Applications in ‘Hyper’ Environments" de John W. Selsky, Jim Goes e Oguz N. Babüroglu, publicado por Organization Studies em Janeiro de 2007.
"Cell 1 is the home of the neoclassical perspective, characterized by a disturbed-reactive environmental texture and conventional interfirm competition. Strategy models in this cell are built around a firm’s industry positioning strategy or distinctive resource-based competencies. The icon is Porter’s five-forces model.O que se passa quadrante 4 (cell 4) é muito interessante.
.
In Cell 2, strategy models are dynamic and assume a disturbed-reactive environmental texture. This is the basis for the ‘guerrilla’ strategy of intensified competition.
...
In Cell 3, the environment is viewed as dynamic, and static strategy models prevail. Firms seek competitive advantage by absorbing external uncertainties in extensive partnering arrangements that are opportunistic and low-trust, such as races to learn more than the partner more quickly. Each partner ‘co-adapts’, and if successful each ‘wins’.
...
Who wins and who loses depends on the competitive advantages that each group of firms creates through collective action’. In Cell 3 models, firms form alliances for the sake of growing bigger to compete more effectively, thereby enhancing firm performance.
...
Cell 4 is the arena for dynamic models of strategy practice in turbulent environments. This cell, we believe, is what scholars have been reaching for in describing the new landscape of strategy and suggesting the usual coping strategies need rethinking. We call this new landscape the hyper environment. Its defining conditions are (1) the stimulation of positive feedback processes in local fields of action that (2) produce emergent structural effects in wider fields of action.
First, in hyper environments actions by the players tend to be self-reinforcing in ways that do not occur in standard competitive environments.
...
A Coevolutionary Relationship - The two conditions of the hyper environment undermine the core contingency assumption in strategy, that a firm’s actions are independent in its extended social field. It is well recognized that the properties of an environment shape strategic responses of firms within it, but outside of social ecology and complexity theories it is less often recognized that strategy practices can alter the texture of the environment itself.
...
The emergent- effects condition of the hyper environment means players are not able to control the consequences of their actions on the environmental texture.[Moi ici: Subitamente recordo Hermann Simon quando este escreve que uma esmagadora maioria dos gestores acredita que o responsável por uma guerra de preço é sempre o concorrente, nunca o próprio]
...
Proposition 1: In hyper environments, the relationship between environmental texture and strategy practices is coevolutionary, not contingent.
...
In Cell 4 the dynamic capabilities reside in systems of firms, or interorganizational networks. These capabilities may be regionally based, industry based or market based. From a Cell 4 vantage point, firms focus on dynamic capabilities ‘not merely to compete better, but especially to coevolve better’."
Imagem e trechos retirados de "Contrasting Perspectives of Strategy Making: Applications in ‘Hyper’ Environments" de John W. Selsky, Jim Goes e Oguz N. Babüroglu, publicado por Organization Studies em Janeiro de 2007.
quinta-feira, agosto 31, 2017
Curiosidade do dia
Esta imagem retirada de um Caderno de Economia do semanário Expresso merece ser bem olhada:
O que dirá Caldeira Cabral?
Repetirá aquela estória?
O que dirá Caldeira Cabral?
Repetirá aquela estória?
"Se a conjuntura explicasse tudo, a aceleração não seria apenas em Portugal, seria um fenómeno europeu e isso não é a realidade", acrescentou.""Fact checking", como escreve a nanda, é coisa que não assiste ao jornalismo português.
Pessoas, não saem de linhas de montagem (parte III)
Parte II.
Ainda em "Why Do We Undervalue Competent Management?" sublinhei:
Ainda em "Why Do We Undervalue Competent Management?" sublinhei:
"False perceptions.
Our research indicates that a surprisingly large number of managers are unable to objectively judge how badly (or well) their firms are run. (Similar biases show up in other settings. For example, 70% of students, 80% of drivers, and 90% of university teachers rate themselves as “above average.”)
.
Consider the average response we got to the question “On a scale from 1 to 10, how well managed is your firm?,” which we posed to each manager at the end of the survey interview. Most managers have a very optimistic assessment of the quality of their companies’ practices. Indeed, the median answer was a 7. Furthermore, we found zero correlation between perceived management quality and actual quality (as indicated by both their firms’ management scores and their firms’ performance), suggesting that self-assessments are a long way from reality.
.
This large gap is problematic, because it implies that even managers who really need to improve their practices often don’t take the initiative, in the false belief that they’re doing just fine.
.
In a variant of this problem, managers may overestimate the costs of introducing new practices or underestimate how much difference they could make."
Sem noção da realidade
Recordo-me muitas vezes de um programa de debate na RTP que aconteceu há muitos anos. Debatia-se Camarate e as hipóteses de acidente ou atentado. A certa altura um dos convidados esgrimiu um argumento que para mim, alguém que estudou química com profundidade e gosto, era absurdo. Quase todos os convidados eram advogados ou juristas e debatiam com base em técnicas de retórica ou oratória, com jogos de palavras e sei lá que mais. O que ficou gravado para mim naquele momento, foi o perceber que um comentador habitual de política nos media portugueses estava a usar um argumento que, se fosse verdade, implicava o sucesso da alquimia. Pensei logo na quantidade de temas que não domino e que aquele e outros comentadores comentam com autoridade.
Como não recordar Sérgio Figueiredo e o fim do calçado, ou André Macedo e o fim do têxtil, ou Pais Mamede e os preços mais baratos para exportação do que para o mercado nacional. Sim, o panorama mediático está cheio de gente sem noção da realidade que ocorre no terreno e, por isso, com ou sem intenção malévola, mistifica a realidade.
Ontem encontrei mais outra dessas mistificações típicas de quem está longe da realidade. Neste texto, "Uma década gloriosa para António Costa", um texto lúcido com o qual concordo em muitos aspectos, Manuel Carvalho estatela-se em grande ao escrever:
Como é possível escrever isto?!
Como é possível acreditar que a recuperação dos sectores tradicionais da economia, dizimados pela concorrência externa aconteceu sob a orientação da academia?
A academia passou completamente ao lado desta recuperação porque ela foi feita com base num novo paradigma competitivo. A academia estava, e muita ainda está, tão embrenhada no paradigma anterior, tão prisioneira de modelos tornados obsoletos que nunca teria a liberdade para a tentativa e erro que foi necessário desenvolver até chegar a algo viável.
Basta visitar as fábricas de calçado para perceber que foi gente do terreno, gente sem alternativa de vida que deu a volta, contra os académicos que previam o Armagedão. Basta visitar as fábricas têxteis e perceber que foi uma revolução bottom-up, como aqui relatei inúmeras vezes, enquanto a direcção da associação patronal do sector combatia o Paquistão e apelava ao proteccionismo, as pessoas do terreno deram a volta.
BTW, recordar a passerelle.
Como não recordar Sérgio Figueiredo e o fim do calçado, ou André Macedo e o fim do têxtil, ou Pais Mamede e os preços mais baratos para exportação do que para o mercado nacional. Sim, o panorama mediático está cheio de gente sem noção da realidade que ocorre no terreno e, por isso, com ou sem intenção malévola, mistifica a realidade.
Ontem encontrei mais outra dessas mistificações típicas de quem está longe da realidade. Neste texto, "Uma década gloriosa para António Costa", um texto lúcido com o qual concordo em muitos aspectos, Manuel Carvalho estatela-se em grande ao escrever:
"É bom que António Costa sublinhe a importância da educação e da ciência, uma feliz recuperação das políticas de Mariano Gago que, ao contrário do que a direita neoliberal apregoava, foram decisivas para que a agricultura, a têxtil ou o calçado sejam o que são hoje."Extraordinária mistificação!!!
Como é possível escrever isto?!
Como é possível acreditar que a recuperação dos sectores tradicionais da economia, dizimados pela concorrência externa aconteceu sob a orientação da academia?
A academia passou completamente ao lado desta recuperação porque ela foi feita com base num novo paradigma competitivo. A academia estava, e muita ainda está, tão embrenhada no paradigma anterior, tão prisioneira de modelos tornados obsoletos que nunca teria a liberdade para a tentativa e erro que foi necessário desenvolver até chegar a algo viável.
Basta visitar as fábricas de calçado para perceber que foi gente do terreno, gente sem alternativa de vida que deu a volta, contra os académicos que previam o Armagedão. Basta visitar as fábricas têxteis e perceber que foi uma revolução bottom-up, como aqui relatei inúmeras vezes, enquanto a direcção da associação patronal do sector combatia o Paquistão e apelava ao proteccionismo, as pessoas do terreno deram a volta.
BTW, recordar a passerelle.
O contexto tem muita força (parte VIII)
Parte I, parte II, parte III, parte IV, parte V, parte VI e parte VII.
Outro artigo citado em "Strategic Planning in Turbulent Environments: A Social Ecology Approach to Scenarios" de Rafael Ramírez e John W. Selsky, publicado por Long Range Planning em 2014, é "Contrasting Perspectives of Strategy Making: Applications in ‘Hyper’ Environments" de John W. Selsky, Jim Goes e Oguz N. Babüroglu, publicado por Organization Studies em Janeiro de 2007 de onde retirei:
Outro artigo citado em "Strategic Planning in Turbulent Environments: A Social Ecology Approach to Scenarios" de Rafael Ramírez e John W. Selsky, publicado por Long Range Planning em 2014, é "Contrasting Perspectives of Strategy Making: Applications in ‘Hyper’ Environments" de John W. Selsky, Jim Goes e Oguz N. Babüroglu, publicado por Organization Studies em Janeiro de 2007 de onde retirei:
"Revolutionary change, increasing volatility and blurring of boundaries in many industries have stimulated two lines of extension of the core neoclassical perspective."Como não pensar logo neste exemplo: "Mayweather e McGregor causam pior fim de semana nas bilheteiras em 16 anos"
"Conflating turbulence with intense competitive challenges reveals two problematic assumptions. One assumption is that strategy is competition, that is, a firm’s key relations with other firms are competitive (or hypercompetitive) and competitive behaviour is directed at other industry players. However, competitive actions may not always be appropriate, and direct effects of competitive actions — as well as unintended higher-order consequences — may not be con- fined to other industry actors. The other assumption is that the competitive ground is considered stable enough for familiar kinds of competitive behaviour, albeit speeded up or more focused.
...
The logical conclusion of conflating turbulence with competitive challenges is that ‘the more turbulent the environment the more aggressive must be the firm’s response’. As we discuss below, such ‘proactive’ responses may produce problematic unintended consequences in extended social fields."
Para alguém como eu que tem pavor dos Dick Dastardly que passam a vida a ver motards e que não seguem o meu querido "Live and let live" isto é importante.
Continua.
quarta-feira, agosto 30, 2017
Curiosidade do dia
Toda a gente em Portugal aprendeu durante os anos da troika a assimetria que existe entre as receitas e as despesas do Estado.
Quando a actividade económica baixa as receitas do Estado baixam mas é crime, de lesa-constituição, reduzir as despesas desse mesmo Estado por causa dos direitos adquiridos. Assim, torna-se inevitável um aumento de impostos que castiga mais ainda a actividade económica.
Hoje, ao ler "Pensões custam mais 860 milhões em 2018 mesmo sem novas medidas", pensando na demografia portuguesa e na "tragédia do poder", com a sua espiral de benesses eleitorais como se não houvesse amanhã, deixei o sentimento do fragilismo militante que nos governa, mergulhar profundamente em toda a sua exuberante irresponsabilidade no meu consciente.
Há dias alguém escrevia o óbvio escondido, não há nenhum RAP com capacidade de o revelar, talvez porque muitos esperam ainda ganhar muito até à próxima crise, mesmo sabendo que de forma insustentável:
Quando a actividade económica baixa as receitas do Estado baixam mas é crime, de lesa-constituição, reduzir as despesas desse mesmo Estado por causa dos direitos adquiridos. Assim, torna-se inevitável um aumento de impostos que castiga mais ainda a actividade económica.
Hoje, ao ler "Pensões custam mais 860 milhões em 2018 mesmo sem novas medidas", pensando na demografia portuguesa e na "tragédia do poder", com a sua espiral de benesses eleitorais como se não houvesse amanhã, deixei o sentimento do fragilismo militante que nos governa, mergulhar profundamente em toda a sua exuberante irresponsabilidade no meu consciente.
Há dias alguém escrevia o óbvio escondido, não há nenhum RAP com capacidade de o revelar, talvez porque muitos esperam ainda ganhar muito até à próxima crise, mesmo sabendo que de forma insustentável:
"“feliz o país que em tempo de (alguma) bonança e crescimento, pensa na próxima recessão”.
.
Claro que ninguém sabe quando ocorrerá a próxima recessão. Apenas sabemos que ela ocorrerá inevitavelmente."
"the less marketing à la vingtième siècle is needed"
"We need a shift in the way many of us think about our roles as marketers and entrepreneurs.
.
Customers means anyone who takes an action with you, whether it's paid or not. It's not wrong, but it's incomplete, on two dimensions.
.
The first dimension is that the transaction is just the beginning; fulfillment is what grows customer lifetime value.
...
The second dimension is that we live in an interrelated world, and one person's end of cycle dovetails with another person's beginning of cycle.
Ultimately, the more success you experience and create, the less marketing matters. This means we shouldn't settle for the transaction of making a sale. We need to aim to give our customers a transformation, whether in the form of solving their problems or providing delight."Combinar o último sublinhado com a ascensão da importância da economia das experiências e com os seguintes textos.
Primeiro, "The Visibility Paradox":
"You don’t need to look far to see that we’re expending a lot of time and resources metaphorically waving our arms in an attempt to be seen. The irony is the best way to be seen is to get better at seeing.Segundo, "Everything Social Marketers Need to Know About Micro-Influencers":
.
When we become more interested, empathetic and generous, we not only see the opportunities others miss, we also do our best work in the service of others. There will always be a place in the world for, as broadcaster Krista Tippett says, ‘voices not shouting to be heard’. We build businesses we’re proud of by ignoring the noise and getting in touch with our humanity."
"When it comes to your social media strategy, bigger isn’t always better.Talvez aquele "the less marketing matters" deva ser substituído por algo como "the less marketing à la vingtième siècle is needed".
...
In contrast to more well-known or celebrity influencers, micro-influencers are everyday social media users with smaller audiences.
...
82 percent of consumers were “highly likely” to follow a recommendation made by a micro-influencer.
...
They are perceived to be more trustworthy than celebrities
...
micro-influencers are 6.7 times more efficient per engagement than influencers with larger followings. The down-to-earth relatability of everyday people is something huge social media influencers can’t buy.
.
With micro-influencers, “You are spreading the word about your brand through lots of different ‘everyday’ people in a seemingly organic way,”
...
“Because they are personally invested in their crafts, micro-influencers are trusted sources of recommendations for followers, ... Micro-influencers have a genuine interest in the topics they post about—something that comes across in their content."
Trecho inicial retirado de "Want Happier Customers? Focus on Transformation, Not Transaction".
Pessoas, não saem de linhas de montagem (parte II)
Depois de ter escrito "Pessoas, não saem de linhas de montagem" onde chamo a atenção para a heterogeneidade das pessoas:
- Touché!
Ora vejamos:
"Julgo que a maior fonte de variabilidade reside nos recursos humanos. Há empresas com que trabalho num dia, em que nunca proporia certas práticas de gestão que recomendei a outras no dia anterior. Diferentes pessoas, diferentes arcaboiços psicológicos, diferentes objectivos pessoais e profissionais, diferentes níveis de abstracção."Em "Why Do We Undervalue Competent Management?" não pude deixar de sentir:
- Touché!
Ora vejamos:
"It’s a truism among strategists that you can’t compete on the basis of better management processes because they’re easily copied. Operational excellence is table stakes in the competitive marketplace.Ou seja:
...
Organizations need competent management just as much as they need analytical brilliance. We should stop teaching business school students that operational issues are beneath the CEO—and should encourage firms to invest in strengthening management throughout the organization.
...
If you look at the data, it becomes clear that core management practices can’t be taken for granted. There are vast differences in how well companies execute basic tasks like setting targets and grooming talent, and those differences matter: Firms with strong managerial processes perform significantly better on high-level metrics such as productivity, profitability, growth, and longevity. In addition, the differences in the quality of those processes—and in performance—persist over time, suggesting that competent management is not easy to replicate.
.
Nobody has ever argued that operational excellence doesn’t matter. But we contend that it should be treated as a crucial complement to strategy—and that this is true now more than ever. After all, if a firm can’t get the operational basics right, it doesn’t matter how brilliant its strategy is."
"Achieving managerial competence takes effort, though: It requires sizable investments in people and processes throughout good times and bad. These investments, we argue, represent a major barrier to imitation."Recordei logo o artigo de Porter, "What is Strategy?" ... A heterogeneidade dos recursos humanos pode ser uma importante barreira contra a imitação.
O contexto tem muita força (parte VII)
Parte I, parte II, parte III, parte IV, parte V e parte VI.
Continuando a leitura do artigo "Strategy as Ecology":
E imaginar as empresas que trabalhavam a sua oferta como uma commodity e que se viram batidas nesse campeonato pela chegada do low-cost chinês...a ter de mudar de estratégia, a ter de pensar num ecossistema.
Continuando a leitura do artigo "Strategy as Ecology":
"A company’s choice of ecosystem strategy— keystone, physical dominator, or niche—is governed primarily by the kind of company it is or aims to be. But the choice also can be affected by the business context in which it operates: the general level of turbulence and the complexity of its relationships with others in the ecosystem.Qual o quadrante que faz mais sentido para a sua empresa?
.
If your business faces rapid and constant change and, by leveraging the assets of other firms, can focus on a narrowly and clearly defined business segment, a niche strategy may be most appropriate. You can develop your own specialized expertise, which will differentiate you from competitors and, because of its simple focus, foster the unique capabilities and expertise you need to weather the turbulence of your environment.
.
If your business is at the center of a complex network of asset-sharing relationships and operates in a turbulent environment, a keystone strategy may be the most effective. By carefully managing the widely distributed assets your company relies on—in part by sharing with your business partners the wealth generated by those assets—you can capitalize on the entire ecosystem’s ability to generate, because of its diversity, innovative responses to disruptions in the environment.
.
If your business relies on a complex network of external assets but operates in a mature industry, you may choose a physical dominator strategy. Because the environment is relatively stable and the innovation that comes with diversity isn’t a high priority, you can move to directly control the assets your company needs, by acquiring your partners or otherwise taking over their functions. A physical dominator ultimately becomes its own ecosystem, absorbing the complex network of interdependencies that existed between distinct organizations, and is able to extract maximum short-term value from the assets it controls. When it reaches this end point, an ecosystem strategy is no longer relevant.
.
If, however, your business chooses to extract maximum value from a network of assets that you don’t control—the value dominator strategy—you may end up starving and ultimately destroying the ecosystem of which you are a part. This makes the approach a fundamentally flawed strategy.
If you have a commodity business in a mature and stable environment and operate relatively independently of other organizations, an ecosystem strategy is irrelevant— although that may change sooner than you think."
E imaginar as empresas que trabalhavam a sua oferta como uma commodity e que se viram batidas nesse campeonato pela chegada do low-cost chinês...a ter de mudar de estratégia, a ter de pensar num ecossistema.
terça-feira, agosto 29, 2017
Curiosidade do dia
reversões têm custos. temos pena— Carlos P da Cruz (@ccz1) August 4, 2017
é a isso q se chama: opções políticashttps://t.co/cW8yA2dSc8
política = fazer opções = valorizar umas coisas em detrimento de outras https://t.co/ZpaUACm5Z2 https://t.co/KSKDVh5LYW— Carlos P da Cruz (@ccz1) June 22, 2017
Álvaro Vaz tem de ser internado, a dizer q ñ há €€ para tudo, q é preciso fazer opções. entranho tempo este em q o bom senso faz espécie— Carlos P da Cruz (@ccz1) September 28, 2012
Imaginem quantos telejornais, quantos fóruns radiofónicos, quantos Pros e Contras teriam como tema este artigo "Como a austeridade afecta hospitais, militares e escolas em Portugal" no tempo "da outra senhora"
Nem de propósito, a última reflexão de Joaquim Aguiar em "A tragédia do poder":
"A economia é uma ciência social triste, porque trata da afectação de recursos escassos a finalidades alternativas, o que implica a eterna frustração que é a condenação dos que foram expulsos do paraíso. Porque os recursos são escassos, o que se afectar a uma finalidade já não poderá ser aplicado ou desviado para outra.
...
O Estado é o palco em que se projectam estas ilusões - a ilusão de que o poder político pode satisfazer todas as necessidades da sociedade como se os recursos não fossem escassos e isso não implicasse beneficiar uns e prejudicar outros, e a ilusão de que a política, desde que legitimada em eleições, não tem de reconhecer que os recursos são escassos, pelo menos para os que elegeram esse poder.
.
Mas há os que sabem distinguir a ilusão da realidade e capturam o Estado para, invocando o interesse geral, satisfazerem os seus interesses particulares, protegidos pela legitimidade que os iludidos lhes atribuíram. São os que capturam o Estado que mantêm a tragédia em cena, fragilizando a economia e a sociedade, e beneficiando com isso."
Por outro lado, os médicos ganham mais. Foi uma escolha política. https://t.co/XrOPFtrFkz— Carlos G. Pinto (@carlosgpinto) August 29, 2017
Paciência estratégica porque todas as estratégias são provisórias
Quando li pela primeira vez que a Amazon ia comprar a Whole Foods interroguei-me sobre o que iriam fazer com a marca.
Sabia que a Whole Foods estava a perder clientes, intuía que teriam de mudar algo e pensava que talvez precisassem de alguma paciência estratégica para descobrir esse novo algo. Por isso, só consegui assentar em duas coisas: tempo para fazer mudanças e aproveitar as lojas físicas para servirem de apoio às lojas online.
Agora, em "Amazon Is Changing How You Buy Groceries at Whole Foods (Starting With Cheaper Prices)" encontro algo que faz sentido, sobretudo depois de ter lido há dias o texto que deu origem ao postal "Quando a diferenciação sofre uma erosão":
Recordar:
Sabia que a Whole Foods estava a perder clientes, intuía que teriam de mudar algo e pensava que talvez precisassem de alguma paciência estratégica para descobrir esse novo algo. Por isso, só consegui assentar em duas coisas: tempo para fazer mudanças e aproveitar as lojas físicas para servirem de apoio às lojas online.
Agora, em "Amazon Is Changing How You Buy Groceries at Whole Foods (Starting With Cheaper Prices)" encontro algo que faz sentido, sobretudo depois de ter lido há dias o texto que deu origem ao postal "Quando a diferenciação sofre uma erosão":
"Whole Foods, meanwhile, gets to exhale. Before the deal, the chain was under intense pressure from shareholders to improve its financial results and figure out how to stop customers from going to lower-priced supermarkets to buy natural foods."Jeff Bezos é conhecido por ser adepto da paciência estratégica.
Recordar:
- Turn, turn, turn (Março de 2017)
- Turn, turn, turn (parte II) (Março de 2017)
BTW, ainda este trecho:
"The deal gives Amazon more than 465 physical stores in the U.S., Canada and the U.K. Before the acquisition, Amazon had a small brick-and-mortar presence with less than a dozen bookstores, a prototype convenience store in Seattle and pickup locations in some cities near college campuses. The tie-up may also give the Seattle-based company valuable data on how people shop in stores, where the vast majority of retail sales still take place. Amazon is an expert in using data on past purchases and browsing to offer suggestions that might make people buy more, and could start applying that in stores as well as online."
A alternativa que não foi seguida pela imprensa
"“We are breathing new life into the Czech glass industry,” says Pavel Weiser, the glassmaker’s owner.A mesma alternativa que o calçado e o mobiliário desenvolveram com sucesso para fugir ao rolo compressor do low-cost chinês: subir na escala de valor.
.
Weiser’s company, Verreum, has drawn a global following by marrying traditional craftsmanship with 21st century design and marketing.
...
Czech manufacturers have struggled in the post-Soviet era as state-owned factories were privatized and faced lower-cost competition from China.
...
Verreum leases its space but next year plans to open its own factory. Weiser says sales will grow about 30 percent this year from €1 million in 2016. While the company occupies only a tiny niche in the Czech glassware industry, it provides a lifeline to some suppliers of glassmaking equipment while employing graduates of a local school that trains glassblowers. The plant offers “a completely new work routine,” says Michal Masek, recruited by Verreum after the factory where he worked went bankrupt. “There’s more art and design. Every day is different.”"
A alternativa que não foi seguida pela imprensa: "O anúncio da morte da imprensa desta vez é para levar a sério". Ainda esta semana tivemos um exemplo da descida na escala de valor.
Trechos retirados de "A Czech Producer Buffs Up the Bohemian Glass Industry With a Focus on Design"
O contexto tem muita força (parte VI)
Parte I, parte II, parte III, parte IV e parte V.
Ainda no artigo "Strategy as Ecology", referido na parte V, encontro outra variante relevante para o tema dos ecossistemas:
Ainda no artigo "Strategy as Ecology", referido na parte V, encontro outra variante relevante para o tema dos ecossistemas:
"Keystone organizations play a crucial role in business ecosystems. Fundamentally, they aim to improve the overall health of their ecosystems by providing a stable and predictable set of common assetsAquilo que no artigo é designado por "keystone" é por mim chamado há anos de "pivô":
...
Keystones can increase ecosystem productivity by simplifying the complex task of connecting network participants to one another or by making the creation of new products by third parties more efficient.
...
By continually trying to improve the ecosystem as a whole, keystones ensure their own survival and prosperity. They don’t promote the health of others for altruistic reasons; they do it because it’s a great strategy.
.
Keystones, in many ways, are in an advantageous position. As in biological ecosystems, keystones exercise a systemwide role despite being only a small part of their ecosystems’ mass.
...
Broadly speaking, an effective keystone strategy has two parts. The first is to create value within the ecosystem. Unless a keystone finds a way of doing this efficiently, it will fail to attract or retain members. The second part, as we have noted, is to share the value with other participants in the ecosystem. The keystone that fails to do this will find itself perhaps temporarily enriched but ultimately abandoned.
.
Keystones can create value for their eco-systems in numerous ways, but the first re- quirement usually involves the creation of a platform, an asset in the form of services, tools, or technologies that offers solutions to others in the ecosystem."
- Primeiro, quem é o pivô da vossa procura? (Janeiro de 2013)
- A humidade do mar vai precipitá-las no oceano... (parte II) (Fevereiro de 2013)
- Conseguirá obter uma sinergia co-evolutiva muito mais poderosa (Dezembro de 2013)
- A escolha dos pivôs (parte I) (Fevereiro de 2014)
- A escolha dos pivôs (parte II) (Fevereiro de 2014)
segunda-feira, agosto 28, 2017
Curiosidade do dia
"Desenganem-se aqueles que dizem que défices nulos (entenda-se aqui saldo estrutural nulo) significam cortes de despesa. São duas coisas totalmente separadas e independentes: tanto podemos ter um défice nulo com um Estado que gaste 50% do PIB (ou mais) como com um Estado que gaste 35% (ou até menos).No entanto, o que mais vejo é gente com o descaramento de querer mais despesa e, em simultâneo, menos impostos. Como a grande massa daqueles que querem mais défice e, em simultâneo, menos dívida.
.
A decisão de um saldo estrutural nulo apenas determina qual o nível de carga fiscal que se pretende, dado que a despesa passa a ser financiada por impostos e outras receitas (correntes e de capital).
.
Ou seja, temos, enquanto sociedade e Democracia, que fazer uma escolha: de um lado, quem defende mais despesa (e consequentemente mais impostos) e do outro lado, quem defende menos impostos (e portanto, menos despesa). O que não podemos é continuar a financiar despesa corrente com dívida pública, que mais não é que impostos para o futuro."
Enfim.
Trecho retirado de "O “Consenso orçamental” – Parte II"
Pessoas, não saem de linhas de montagem
No final de Julho numa empresa, perguntaram-me se eu estava de acordo com a prática que seguem de estabelecer objectivos ambiciosos face ao ano anterior.
A minha resposta foi qualquer coisa do tipo: o que vejo são resultados para 2017 abaixo das metas mas muito melhores que os de 2016. Assim, talvez seja de concluir que a vossa prática resulta. Pelo menos convosco resulta.
Entretanto, encontrei e li "Stretch Goals and the Distribution of Organizational Performance" de Michael Shayne Gary, Miles M. Yang, Philip W. Yetton e John D. Sterman, publicado online pela revista Organization Science em Maio de 2017. O artigo é um bocado estranho. Por exemplo:
Ao longo de 30 anos de experiência a trabalhar com muitas empresas, como cliente, como fornecedor e sobretudo como consultor, sempre tenho encontrado muita variabilidade de empresa para empresa. Julgo que a maior fonte de variabilidade reside nos recursos humanos. Há empresas com que trabalho num dia, em que nunca proporia certas práticas de gestão que recomendei a outras no dia anterior. Diferentes pessoas, diferentes arcaboiços psicológicos, diferentes objectivos pessoais e profissionais, diferentes níveis de abstracção. Em cada caso há que procurar co-descobrir o que é que faz mais sentido para cada uma dessas empresas no contexto particular em que operam.
A minha resposta foi qualquer coisa do tipo: o que vejo são resultados para 2017 abaixo das metas mas muito melhores que os de 2016. Assim, talvez seja de concluir que a vossa prática resulta. Pelo menos convosco resulta.
Entretanto, encontrei e li "Stretch Goals and the Distribution of Organizational Performance" de Michael Shayne Gary, Miles M. Yang, Philip W. Yetton e John D. Sterman, publicado online pela revista Organization Science em Maio de 2017. O artigo é um bocado estranho. Por exemplo:
"Second, instead of being evidence that organizations should adopt stretch goals, the small number of successful cases held up as exemplars for the benefits of stretch goals is evidence that stretch goals are not a rule for riches for all organizations.Quase que apetece dizer: Duh!
...
Third, the findings inform the issue of setting appropriate goals for specific contexts. In particular, the results show that whether boards or top management should impose stretch goals on their organization depends on their attitudes toward risk. Those with large appetites for risk may still prefer stretch goals. However, for those who are risk neutral or risk averse, stretch goals may not be desirable because the increase in performance variance—including the risk of failure—and the lower risk-adjusted return achieved by the typical organization outweigh the chances for improvement achieved by a few successful high performers.
...
Preference for stretch versus moderate goals may also be contingent on the nature of the market. In markets characterized by reinforcing feedbacks, such as increasing returns, that lead to winner-take-all dynamics, stretch goals may prove the only path to success: firms must “go for broke or die trying.” However, in markets where multiple firms can coexist, the risks of failure due to stretch goals may dominate, and the watchword should be “live and let live.”
These arguments show how the appropriate goal difficulty level depends on the context."
Ao longo de 30 anos de experiência a trabalhar com muitas empresas, como cliente, como fornecedor e sobretudo como consultor, sempre tenho encontrado muita variabilidade de empresa para empresa. Julgo que a maior fonte de variabilidade reside nos recursos humanos. Há empresas com que trabalho num dia, em que nunca proporia certas práticas de gestão que recomendei a outras no dia anterior. Diferentes pessoas, diferentes arcaboiços psicológicos, diferentes objectivos pessoais e profissionais, diferentes níveis de abstracção. Em cada caso há que procurar co-descobrir o que é que faz mais sentido para cada uma dessas empresas no contexto particular em que operam.
O contexto tem muita força (parte V)
Parte I, parte II, parte III e parte IV.
Em "Strategic Planning in Turbulent Environments: A Social Ecology Approach to Scenarios" de Rafael Ramírez e John W. Selsky, publicado por Long Range Planning em 2014, encontrei uma referência que me despertou curiosidade, "Strategy as Ecology" de Marco Iansiti e Roy Levien, publicado pela Harvard Business Review em Março de 2004.
Como é que tinha passado ao lado de um artigo deste tipo, todo ele em sintonia com o que escrevo neste blogue há anos:
Em "Strategic Planning in Turbulent Environments: A Social Ecology Approach to Scenarios" de Rafael Ramírez e John W. Selsky, publicado por Long Range Planning em 2014, encontrei uma referência que me despertou curiosidade, "Strategy as Ecology" de Marco Iansiti e Roy Levien, publicado pela Harvard Business Review em Março de 2004.
Como é que tinha passado ao lado de um artigo deste tipo, todo ele em sintonia com o que escrevo neste blogue há anos:
"the performance of these two very different firms derives from something that is much larger than the companies themselves: the success of their respective business ecosystems. These loose networks—of suppliers, distributors, outsourcing firms, makers of related products or services, technology providers, and a host of other organizations—affect, and are affected by, the creation and delivery of a company’s own offerings.
.
Like an individual species in a biological ecosystem, [Moi ici: Uma frase que junta dois temas que muito aprecio. A economia como uma continuação da biologia e a vantagem de trabalhar com ecossistemas] each member of a business ecosystem ultimately shares the fate of the network as a whole, regardless of that member’s apparent strength.
...
Your own business ecosystem includes, for example, companies to which you outsource business functions, institutions that provide you with financing, firms that provide the technology needed to carry on your business, and makers of complementary products that are used in conjunction with your own. It even includes competitors and customers, when their actions and feedback affect the development of your own products or processes. The ecosystem also comprises entities like regulatory agencies and media outlets that can have a less immediate, but just as powerful, effect on your business."
Fora do comum
No Caderno de Economia do semanário Expresso do passado dia 19 de Agosto, no meio de um texto designado por "Antecipar o "Pedrógão Grande cibernético" de José Tribolet, encontrei este trecho tão pouco comum numa publicação portuguesa:
Salvar uma empresa con dinheiro dos contribuintes, quando não tem clientes em número suficiente para a sustentar e, contra os trabalhadores das empresas concorrentes.
"Primeiro - Não contar com financiamento directo por parte do Orçamento de Estado. Esta fábrica é para funcionar no mercado. Ou o mercado precisa destes produtos e está disposto a pagar por eles ou nada irá acontecer!"Uma postura bem diferente da normal em Portugal que é mais deste tipo: "BE pede ao Governo para salvar empresa histórica de Tomar"
Salvar uma empresa con dinheiro dos contribuintes, quando não tem clientes em número suficiente para a sustentar e, contra os trabalhadores das empresas concorrentes.
domingo, agosto 27, 2017
"humans are the source of economy"
"This is a future where the human(e) corporate will be defined by its capacity to drive collaborative humane intelligence, agency, care, creation and discovery – not its aggregative efficiency to manage financial capital and procure in scale; these efficiencies are likely to distributed and platformed to the whole economy – with rise of zero overhead platform bureaucracy.Todo este texto "Beyond Labour" está relacionado com a previsão que faço para Mongo como um mundo de artesãos.
.
This is a future in which investing for the human development of an organisation manifests on its asset register.
.
This is a future which embraces a tomorrow, where humans are the source of economy not redundant to its function."
Tendências para a evolução dos media
Trechos retirados de "Future files : 5 trends that will shape the next 50 years" de Richard Watson.
"an increased demand for snack-sized formats and content available in a variety of sizes or lengths. Equally, the old model of edit first and publish second will be reversed, with content being published first and edited second (filtered by the audience). Long copy and rigorous analysis will become a specialist demand available on a pay-per-view basis, with journalists being compensated the same way. [Moi ici: Em linha com o que sempre escrevemos aqui, em vez de competir pelo pelo preço e tentar chegar a milhões, optar por trabalhar para nichos ou tribos underserved] Conversely, people will seek out quality content (judged, increasingly, by external links) regardless of format, length or even language. All of this will also create a high demand for quality search, editing and “sifting” of information and entertainment.
...
Users will shift media to suit their particular requirements. For example, video on demand (or mobile video) will alter the way people watch television, much in the same way that podcasting has already changed the way people listen to radio. Both put the audience squarely in charge of programming. In the future, people will watch, read and listen to what they want, when they want, on any device they want, and content will be designed, edited and personalized for specific physical locations and situations.
...
What are people paying for? The answer is scarcity. If the cost of creating and distributing digital content becomes practically zero, content will be ubiquitous and largely valueless as a result. Personalization and particularly physicalization (e.g. live events and experiences) will, on the other hand, be highly sought after. We will watch movies at home but we will pay more to experience them with other people in a cinema. Add to this a general flight to quality and media such as the best newspapers, magazines, television and radio could do very well in the future.
...
In the future, it will be easier than ever to turn on, tune in and drop out, because while mainstream media channels and events will continue to exist, so too will a plethora of micromedia appealing to every conceivable interest, belief, prejudice and opinion. The top-down model, whereby media owners hold the attention of millions and then sell that attention to other people such as advertisers, is being replaced by companies and individuals who attract the fleeting attention of large, promiscuous audiences and by niche operators who capture the hearts and minds of very tiny audiences.
.
In other words, the media universe is becoming polarized between very large and very small players. Moreover, the content produced by these totally different types of media organization will also be at two extremes, with the larger companies clustering around proven formulae and the smaller operators pushing the boundaries with original ideas. Both will obviously aim to appeal to as large an audience as possible, but only one will be able to survive when the audience is tiny. Equally, anyone stupid or unlucky enough to get caught in the middle will be history."
sábado, agosto 26, 2017
O contexto tem muita força (parte IV)
Parte I, parte II e parte III.
"in a number of sectors today, strategy comes from players across a range of industries, in which they both collaborate and compete.Trechos retirados de "Strategic Planning in Turbulent Environments: A Social Ecology Approach to Scenarios" de Rafael Ramírez e John W. Selsky, publicado por Long Range Planning em 2014.
...
most mainstream strategic planning approaches conflate strategy with competition. The neoclassical approach thus relegates cooperative and collaborative initiatives to a tactical position, marginal to the main strategic activity. Here alliances and joint ventures tend to be undertaken in order for a focal firm to extract value from them for its own goals, at the expense of not only other alliance participants but also other players such as customers and suppliers.
...
greater competitive intensity can damage the wider field of action through negative externalities not absorbed by the producers.
...
When the environment which companies inhabit changes, or is considered that it might soon change, companies engage in strategic renewal efforts to reinvent themselves, ... When they become adept at this, the routines they utilize become dynamic capabilities that can be used repeatedly for their own strategic purposes.
.
the neoclassical approach to strategic planning is challenged by environmental jolts, and by discontinuities and bifurcations. This is because neoclassical approaches rely on competitive patterns (actions and reactions among players) observed in past behavior, and which are extrapolated into the future in terms of forecasts. In addition, the neo-classical view assumes that the broader context for strategic action - the macro situation which envelops the “industry” - will remain stable in the sense that the fundamental structure of the environment will not change as a result of the players' intensified or sped-up competitive actions.
.
The socio-ecological approach to strategic planning is grounded in an open-systems view of an organization's strategic situation. As opposed to the firm as the focal unit of analysis in the neoclassical approach, it is the shared field of interorganizational action that is the core unit of analysis. It is within this broader perspective that the socio-ecological approach seeks to understand the position and behavior of actors (for our purposes, organizations) in that field. For instance, the business ecosystem model offered by Iansiti and Levien, comprised of a central “keystone” firm and complementary firms in dynamic interaction over time, is a step in the direction of a field-based, socio-ecological approach to strategy
...
In the socio-ecological approach, collaborative interactions enjoy a higher profile as integral components of corporate and business strategic planning than in the neoclassical approach. Yet -importantly- the emphasis is not within the “industry”, not on horizontal partnering with competitors, and not on vertical ventures with value-chain partners. Instead, here collaboration is with diverse actors and stakeholders of the broader fields in which organizations operate in order to together engage contextual level forces that affect or may affect all actors in a field.
...
Socio-ecologically based strategic planning acknowledges commercial and competitive challenges, but is more sensitized to macro level disruptions and unpredictable uncertainty. It suggests that, when unpredictable uncertainty becomes the central concern of strategic planners, the strategic situation has shifted into a different, turbulent “texture”, which calls for a different mode of strategic planning."
Acerca de Mongo
"When Voodoo launched, Friefeld said that the team began to realize that they were serving two different markets. The first market is made up of engineering companies that are launching new products and which need to produce a few thousand products for early testing and validation.Voodoo works with these firms to produce the first few thousand enclosures and other parts for their designs. The second market consists of marketing materials and other aesthetic products.Isto encaixa perfeitamente na narrativa acerca da caminhada para esse novo mundo económico que designo por Mongo. Um mundo de diversidade e com cada vez menos necessidade de grandes séries.
.
How can a 3D printing company compete with the $162 billion injection molding market? Voodoo accomplished this by purchasing off-the-shelf 3D printers, which require very little up-front investment when compared to an industrial manufacturing operation. Running a series of print farms, Friefeld said that his startup is cost-competitive with injection molding for runs of up to 10,000 units. For print runs above that, it usually makes more economic sense to have parts made with injection molding.
.
“With Voodoo, there’s no up-front investment,” Friefeld said.“We can get started with the file and get your part the next day, or 10,000 parts in two weeks. We’re fast and we have very little startup costs with our process.That’s all because we’re using 3D printers—digital manufacturing tools that can take in a digital file and produce a physical product with little human interaction. No tool, no tooling, no jigs, no fixtures. File in, product out.”
...
“Ultimately, we will be producing low-volume runs of any manufactured product anywhere in the world,” Friefeld said.“[We’re] starting with plastic today, but we’ll eventually expand into other materials and processes built on top of these digital tools like 3D printers.”"
Há algum tempo discutia-se numa empresa a necessidade de investir numa unidade toda automatizada, ao estilo 4.0, para se especializar na produção de grandes séries. Sinto que os escandalizei quando os tentei convencer a fazerem o contrário: investir numa nova unidade pequena, mas para se concentrar nas pequenas séries.
As empresas grandes pensam nas séries grandes e não dão a atenção suficiente às pequenas séries e a um outro estilo de marketing, de actividade comercial e de produção que requerem. Pensem no Director Comercial de uma empresa grande. Pensem no desafio que ele tem de enfrentar todos os anos de aumentar as vendas para ir ao encontro de objectivos de facturação muito ambiciosos. Pensem como o volume de vendas é muito mais fácil de medir que o lucro unitário obtido com essas mesmas vendas. Pensem como esse Director terá tendência a matar/asfixiar todos os projectos de novos produtos e serviços que não prometam pelo menos X de vendas rapidamente. Julgo que a única hipótese que uma empresa grande tem de fazer a transição para Mongo, é a de criar spinoffs e colocar gente apaixonada e obrigada a passar fome de recursos, à frente desses projectos. (Interessante como esta referência a gente apaixonada me fez recordar este podcast recente de Nassim Taleb, "Nassim Nicholas Taleb on Work, Slavery, the Minority Rule, and Skin in the Game")
Trechos retirados de "Voodoo Automates 3D Printing to Take on Injection Molding"
sexta-feira, agosto 25, 2017
Quando a diferenciação sofre uma erosão...
Há dias li "That Chicken From Whole Foods Isn’t So Special Anymore". Hoje, encontrei dois textos que parecem ser a consequência natural do primeiro:
- UK supermarkets slip after Amazon decision to cut prices at Whole Foods
- Amazon to cut Whole Foods prices, escalating grocery turf war
Quando a diferenciação sofre uma erosão...
O contexto tem muita força (parte III)
Parte I e parte II.
"strategic planning is a process that supports the creation of future value through the identification, definition, production, assessment and application of goals and resources, and by selecting or making one or more chosen market spacesTrechos retirados de "Strategic Planning in Turbulent Environments: A Social Ecology Approach to Scenarios" de Rafael Ramírez e John W. Selsky, publicado por Long Range Planning em 2014.
...
The conventional view of strategic planning, with intellectual roots in neoclassical economics, focuses on working with “predictable” uncertainty, which includes supply, demand and internal process fluctuations (sometimes cyclical) largely resulting from competitive dynamics. Also included are macroeconomic and, increasingly, natural ecological factors that can be reasonably anticipated.
In contrast, a socio-ecological view of strategic planning, with intellectual roots in systems theory and field theory, engages not only with predictable uncertainty but also with Knight's (1921) “unpredictable” uncertainty, including environmental jolts, unforeseen macro-level disruptions and “black swan” events. [Moi ici: Mais uma vez a força do contexto]
...
conventional neoclassically based strategic planning construes uncertainty as commercial challenges to be surmounted through competitive moves, along one or more of four choice vectors - cost-quality, timing and know-how, entry barriers, and financial resources. This form of strategic planning assumes perfect rationality and equal access to information among the competitors. The arena of competition is viewed as the industry, which receives the bulk of the planner's attention, and profit maximization is seen as the goal of each competitor firm engaged in its autonomous strategic pursuits. A more nuanced rendering relaxes the assumptions of perfect rationality and equal information access by acknowledging the constraints of path dependence, as well as the exercise of power and knowledge asymmetries, heterogeneous dynamic capabilities, bounded rationality, behavioral biases, and the possibility of game-changing or “disruptive” innovation moves."
Economia das experiências - dois exemplos
Mais dois exemplos da economia das experiências.
Um primeiro exemplo aplicado ao mundo do futebol, "For a Price, a Chance to Go Beyond a Premier League Curtain":
Um primeiro exemplo aplicado ao mundo do futebol, "For a Price, a Chance to Go Beyond a Premier League Curtain":
"On Monday night, Manchester City unveiled its Tunnel Club, a first of its kind in European soccer. The clue is in the name: For prices starting at 299 pounds per game (about $385), and rising to £15,000 (about $19,240) per season for so-called premium access, fans can buy access to the area around the tunnel that leads from the Etihad Stadium’s dressing rooms to the pitch itself.E um segundo aplicado às compras das empresas que trabalham o B2C, "The Experience Economy and Procurement":
.
For their money, they are rewarded with the chance to see the players from each team as they enter the stadium. They can watch them file from their changing rooms before the start of each half, and see them return at halftime and full time. They get to see Guardiola remonstrating with the match officials. They get a glimpse behind the curtain.
...
“experiential purchases are more gratifying, on average, than material purchases.” Experiences, rather than things, “facilitate more social connections, are more tied to the self, and are experienced more on their own terms.” In other words, doing rather than buying things makes you happier.
The logic behind the Tunnel Club, what makes it valuable, is that it heightens the experience of going to see a soccer game. It is not simply “turning up to your seat 10 seconds before kickoff, and leaving just as quickly afterwards,” as Cook said. It is more than that.
.
City did not just transplant the idea it found in Arlington, Tex., the home of the Cowboys, straight into England. Berrada and his team tried to tweak it, taking ideas from Formula One — where a V.I.P. tour of the paddock, as the drivers and cars are getting ready for the race, is a tradition — and from concerts, where backstage access is sold as an additional benefit.
.
Those paying the premium fees for City’s Tunnel Club, then, are not only offered a tactical briefing before the game — delivered by two Manchester City analysts — but a question-and-answer session with Brian Kidd, one of Guardiola’s coaches. There is a private area, by the side of the field, from which they can watch the teams warm up. During those moments, they not only have the best view in the house, they can also place their feet on the same artificial turf that lines the side of the field. It is a sensory nod to the overall impression: You are part of the action, you see what the players see, you feel what the players feel.
.
After the game, they can see Guardiola and his Everton counterpart, Ronald Koeman, give their postgame interviews to the news media. And after initial resistance from Guardiola, Tunnel Club members at future games will be able to watch an additional interview with a player before anyone else.
...
City’s Tunnel Club, along with its forthcoming twin at Tottenham, is a natural extension of that trend. Fans do not want to sit and watch a game, they want to feel part of an event. They do not want to consume content, but to create it, too. They do not want just to be closer to the players but to be able to feel what it is like to be the players.
.
The appeal of the Tunnel Club is not that it is an aquarium. It instead offers the chance to know how it is for the fish."
"For many years, cost savings was considered to be the primary – and, in some cases, only – objective of the procurement function.
.
Don’t get me wrong, cost savings still represents a relevant procurement contribution. But it should not be considered the one trick of the procurement pony.
.
A myopic, profession-wide focus on cost savings makes an incorrect assumption. That assumption is that every organization competes on low cost to the consumer and that procurement cost savings enables profit improvement in a tight market.
...
Markets and the businesses that comprise them are increasingly joining the “experience economy.” The experience economy is one in which consumers value how a company, brand, product or service makes them feel as their customer.
.
These experience-chasing consumers don’t make comparisons based on price alone. They don’t select a supplier, service provider, store, or product because it is one penny cheaper than the competition.
.
Instead, they value a unique feeling that they get. They want an experience that they can rave about. And social media’s ever-growing portion of what is considered “real life” only magnifies the desire for a rave-worthy experience.
...
As such, the experience economy has been transforming procurement. Procurement decisions and supplier selections now need to be made based on how positively a decision or selection affects the consumer.
...
- If there’s competition, how does your organization compete? On lowest price? On who creates the more rave-worthy consumer experience? Or something else?
- If competition is based on consumer experience, what is the target experience like for the consumer? What contributes to that experience? How can procurement decisions contribute positively to that experience? And are any procurement decisions currently being made that are contrary to that experience?
- At what stage of the experience economy transformation is your organization in? Are you moving towards making your organization, brand, product, or service more of an experience-oriented purchase for your consumers? Are you standing still? Or, worse, is your organization drifting more towards the airline mentality of “customer service” than towards being a leader in the experience economy?"
quinta-feira, agosto 24, 2017
Mas claro, eu só sou um anónimo engenheiro da província (parte II)
Os amigos da Junqueira, gente que recordo aqui:
Isto é tão arcaico que até arrepia:
"Temos, de facto, um grande problema da cauda. Não é apenas um problema de má gestão. É um problema de pequenez. Hoje em dia, na grande parte das actividades, a escala é muito importante. Na China, uma empresa pequena não deve ter menos de mil trabalhadores e, portanto, isso faz uma diferença muito grande devido às economias de escala. Se em algumas actividades não é significativa, no geral, as empresas pequenas, em Portugal, não têm escala para ser competitivas.
...
Se for possível substituir essa cauda, seja através de concentrações, seja através de substituições, fazendo as mesmas actividades de uma forma mais eficiente, temos uma oportunidade de aumentar a produtividade da economia"
São gente formatada pelo mundo que existia quando tinham 20 anos de idade. Hoje, com Mongo cada vez mais entranhado, um mundo económico com outras regras, ou outras vantagens competitivas, acontecem estas coisas: "Little Noticed, Small Companies With A Worldwide Reach Explode":
"There are still many legal obstacles – shipping, and customs, for instance — for small businesses that want to sell across borders. But technology is helping to enable a new kind of company: the micro-multinational, tiny companies that can piece together their markets from like-minded consumers across regions.
...
technology – including social media – is leveling the landscape for small businesses."
O contexto tem muita força (parte II)
Quando escrevi a Parte I, certamente influenciado por "Densidade e ecossistemas" e "the emerging organizational form for the 21st century", tinha previsto uma outra parte II - basta ver o marcador utilizado nessa parte I.
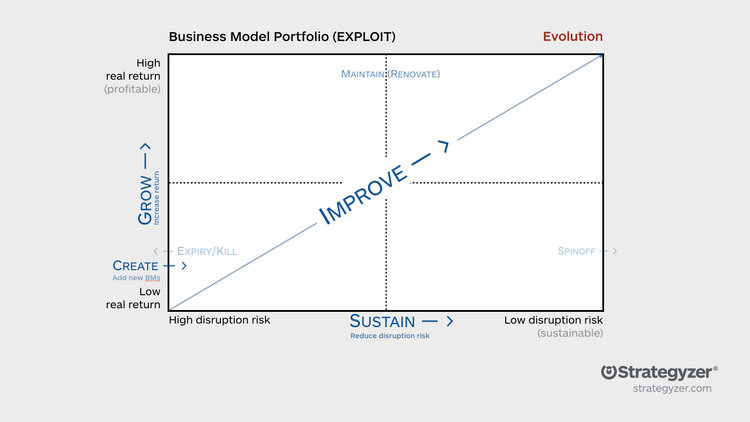
Entretanto, ontem ao final da tarde, quando ia a sair do escritório ouvi este texto "Business Model Portfolio Part 1: Manage The Existing Business":
Entretanto, ontem ao final da tarde, quando ia a sair do escritório ouvi este texto "Business Model Portfolio Part 1: Manage The Existing Business":
"2. Sustainability or disruption risk: How sustainable is your business model, and how likely is it to be disrupted? Models at risk may be very established businesses, but prone to disruption for technology, market, or regulatory changes. Those companies sit on the left hand side. Strong business models with moats to protect them on the other hand are very unlikely to be disrupted. They sit on the right hand side."Mais uma vez a importância do contexto. Não basta ser querido pelos clientes quando estes podem ser empurrados do mercado.
quarta-feira, agosto 23, 2017
"the emerging organizational form for the 21st century"
Ao ler "Creating the competitive edge: A new relationship between operations management and industrial policy" publicado por Journal of Operations Management 49-51 (2017), encontro outro trecho em sintonia com Normann e Ramirez:
"The theoretical underpinning of manufacturing strategy has moved from process choice to a resource-based view, reflecting the growing importance of learning, innovation and idiosyncratic firm- and network-level capabilities.Richard Normann e Rafael Martinez em "Designing Interactive Strategy" escrevem:
...
The unit of analysis in manufacturing strategy has shifted from the plant or firm to the supply network, with supply chain management growing as a domain of OM research from the mid-1990s to the late 2000s
...
Operations are now seen by some as fundamentally inter-organizational. Furthermore, whereas plant-level manufacturing strategy approaches and, to some extent, supply chain management sought to design and control the whole system directly, fragmented networks are perhaps better understood as complex adaptive systems in which any one firm has only local and partial control... the emerging organizational form for the 21st century, rather than the multi-firm network, is the ‘collaborative community’. As such, the ‘institutional architecture’ in which such adaptive systems and communities operate becomes an increasingly important ingredient in manufacturing firms' business landscape."
"strategy is the way a company defines its business and links together the only two resources that really matter in today’s economy: knowledge and relationships or an organization’s competencies and customers.E repito a citação de ontem:
.
But in a fast-changing competitive environment, the fundamental logic of value creation is also changing and in a way that makes clear strategic thinking simultaneously more important and more difficult. Our traditional thinking about value is grounded in the assumptions and the models of an industrial economy. According to this view, every company occupies a position on a value chain. Upstream, suppliers provide inputs. The company then adds value to these inputs, before passing them downstream to the next actor in the chain, the customer (whether another business or the final consumer). Seen from this perspective, strategy is primarily the art of positioning a company in the right place on the value chain—the right business, the right products and market segments, the right value-adding activities.
.
Today, however, this understanding of value is as outmoded as the old assembly line that it resembles and so is the view of strategy that goes with it. Global competition, changing markets, and new technologies are opening up qualitatively new ways of creating value."
"In so volatile a competitive environment, strategy is no longer a matter of positioning a fixed set of activities along a value chain. Increasingly, successful companies do not just add value, they reinvent it. Their focus of strategic analysis is not the company or even the industry but the value-creating system itself, within which different economic actors—suppliers, business partners, allies, customers—work together to co-produce value. Their key strategic task is the reconfiguration of roles and relationships among this constellation of actors in order to mobilize the creation of value in new forms and by new players. And their underlying strategic goal is to create an ever-improving fit between competencies and customers."
Acordar para o potencial deste mercado
Neste artigo, "The Future of the German Discount Fitness Market", saliento:
Recordando este postal recente, "Idade e consumo", acredito que muita gente em Portugal ainda não acordou para o potencial deste mercado. Recordar o mundo das doenças crónicas.
"the market segmented into four price categories:E sublinho: "Health-related: 60 EUR/month"
- Discount: 20 EUR/month
- Premium discount: 39 EUR/month
- Health-related: 60 EUR/month
- Premium: >60 EUR/month"
Recordando este postal recente, "Idade e consumo", acredito que muita gente em Portugal ainda não acordou para o potencial deste mercado. Recordar o mundo das doenças crónicas.
O contexto tem muita força
Há dias que volta e meia me vem ao pensamento o facto de muitas empresas desaparecerem não porque foram mal geridas, não porque tiveram uma gestão criminosa, não porque não se importavam com os seus clientes, não porque os seus clientes não gostavam delas mas simplesmente porque o mundo mudou demasiado depressa e sem aviso prévio.
O exemplo das fábricas de calçado portuguesas que trabalhavam para o mercado nacional, para as sapatarias de rua, quando os centros comerciais apareceram e liquidaram as sapatarias de rua as fábricas de calçado não tiveram hipótese.
O exemplo de tantas e tantas empresas portuguesas que trabalhavam para o sector não-transaccionável e que chocaram com estrondo contra uma parede, quando uma sociedade viciada em dívida viu as fontes de endividamento subitamente secarem.
O exemplo das empresas portuguesas que tinham uma actividade interessante a exportar fruta para o mercado russo e que em 2014, subitamente, ficaram impossibilitadas de o continuar a fazer na sequência das sanções da UE à Rússia por causa da situação na Ucrânia.
O exemplo de um empresário que tinha montado um negócio com sucesso numa cidade do interior, a vender veículos todo o terreno, e que subitamente viu o mercado desaparecer quando o ministro Pina Moura (?) alterou a fiscalidade desses veículos (o choque foi tão grande que acabou por emigrar para o Canadá).
O exemplo das fábricas de calçado portuguesas que trabalhavam para o mercado nacional, para as sapatarias de rua, quando os centros comerciais apareceram e liquidaram as sapatarias de rua as fábricas de calçado não tiveram hipótese.
O exemplo de tantas e tantas empresas portuguesas que trabalhavam para o sector não-transaccionável e que chocaram com estrondo contra uma parede, quando uma sociedade viciada em dívida viu as fontes de endividamento subitamente secarem.
O exemplo das empresas portuguesas que tinham uma actividade interessante a exportar fruta para o mercado russo e que em 2014, subitamente, ficaram impossibilitadas de o continuar a fazer na sequência das sanções da UE à Rússia por causa da situação na Ucrânia.
O exemplo de um empresário que tinha montado um negócio com sucesso numa cidade do interior, a vender veículos todo o terreno, e que subitamente viu o mercado desaparecer quando o ministro Pina Moura (?) alterou a fiscalidade desses veículos (o choque foi tão grande que acabou por emigrar para o Canadá).
terça-feira, agosto 22, 2017
Densidade e ecossistemas
Ao ler "Creating the competitive edge: A new relationship between operations management and industrial policy" publicado por Journal of Operations Management 49-51 (2017), encontro uma citação de uma velha conhecida minha, Suzanne Berger:
“rich and diverse set of complementary capabilities in the industrial ecosystem: suppliers, trade associations, industrial collective research consortia, industrial research centers, Fraunhofer Institutes, university-industry collaborative, technical advisory committees. It's impossible to understand the different fates of manufacturing in the United States and Germany without comparing the density and richness of the resources available in the industrial ecosystem across much of Germany to the thin and shrinking resources available to U.S. manufacturers across much of our country”Ao ver o termo ecossistema, (palavra usada com especial carinho neste blogue), ao ver o desfilar de actores que povoam os meus esquemas sobre ecossistemas da procura (Malta da ISO 9001:2015, estão a ver porque aprecio a cláusula 4.2 da norma? E como a aprecio!) associados à palavra densidade não pude deixar de imediatamente recordar dois nomes: Richard Normann e Rafael Martinez e o seu "Reframing Business: When the Map Changes the Landscape". Bastou uma pesquisa no Google para chegar a "Designing Interactive Strategy":
"In so volatile a competitive environment, strategy is no longer a matter of positioning a fixed set of activities along a value chain. Increasingly, successful companies do not just add value, they reinvent it. Their focus of strategic analysis is not the company or even the industry but the value-creating system itself, within which different economic actors—suppliers, business partners, allies, customers—work together to co-produce value. Their key strategic task is the reconfiguration of roles and relationships among this constellation of actors in order to mobilize the creation of value in new forms and by new players. And their underlying strategic goal is to create an ever-improving fit between competencies and customers.E as suas ideias acerca das constelações:
...
The result is an integrated business system that invents value by matching the various capabilities of participants more efficiently and effectively than was ever the case in the past.
.
What is so different about this new kind of value? One useful way to describe it is that value has become more dense. Think of density as a measure of the amount of information, knowledge, and other resources that an economic actor has at hand at any moment in time to leverage his or her own value creation. Value has become more dense in that more and more opportunities for value creation are packed into any particular offering."
"IKEA is more than a link on a value chain. It is the center of a constellation of services, goods, and design.
.
The image of a value chain fails to capture the complexity of roles and relationships in the IKEA business system. IKEA did not position itself to add value at any one point in a predetermined sequence of activities. Rather, IKEA set out systematically to reinvent value and the business system that delivers it for an entire cast of economic actors. The work-sharing, co-productive arrangements the company offers to customers and suppliers alike force both to think about value in a new way—one in which customers are also suppliers (of time, labor, information, and transportation), suppliers are also customers (of IKEA’s business and technical services), and IKEA itself is not so much a retailer as the central star in a constellation of services, goods, design, management, support, and even entertainment. The result: IKEA has succeeded, arguably, in creating more value per person (customer, supplier, and employee) and in securing greater total profit from and for its financial and human resources than all but a handful of other companies in any consumer industry."
Evolução mensal do desemprego 07-17
Tendo em conta os números do IEFP relativos ao passado mês de Julho, foi possível construir estes gráficos da evolução mensal do desemprego para 9 sectores de actividade da economia portuguesa:
Os números mostram que o desemprego continua a baixar mas agora em clara desaceleração face ao ritmo homólogo de 2016. Apenas no fabrico de automóveis a quebra está mais forte.
Na maioria dos sectores a desaceleração começou em Maio e continuou por Junho e Julho. Algo que parece conciliar-se com a evolução do PIB no 2º trimestre.
Os números mostram que o desemprego continua a baixar mas agora em clara desaceleração face ao ritmo homólogo de 2016. Apenas no fabrico de automóveis a quebra está mais forte.
Na maioria dos sectores a desaceleração começou em Maio e continuou por Junho e Julho. Algo que parece conciliar-se com a evolução do PIB no 2º trimestre.
segunda-feira, agosto 21, 2017
Co-criação de valor - uma fonte
Quando escrevo sobre Mongo, sobre um mundo de artesãos, um mundo de mais proximidade, um mundo de mais customização, um mundo de menos vómito industrial, um mundo de mais significados, penso no aumento da co-criação e penso que esta pode ser realmente uma vantagem competitiva que as PME podem usar para viverem e terem sucesso. Acredito mesmo nisto:
Uma boa fonte de informação sobre o "estado da arte"
"Value cocreation has long been praised as the next source of competitive advantage for service providers in the 21st century. The value of focusing on value cocreation as a source of competitive advantage lies in the interactions service providers develop with their customers and their potential to generate value for their customers. These interactions present a certain level of intimacy with the service provider’s customers, ensuring that they are difficult to replicate for competitors, and can yield long-term benefits such as customer loyalty and high lifetime share of wallet"Por isso, recomendo vivamente a leitura de "Value cocreation in service interactions: Dimensions and antecedents" de Carmen Neghina, Marjolein C. J. Caniëls e Josée M. M. Bloemer, publicado por Marketing Theory, Volume: 15 issue: 2, page(s): 221-242, 2015.
Uma boa fonte de informação sobre o "estado da arte"
Subscrever:
Mensagens (Atom)